The Science Behind Hormonal Agent Guideline: Insights From an Endocrinologist
The Science Behind Hormonal Agent Regulation: Insights From an Endocrinologist provides a detailed expedition of the complex procedures included in hormonal agent regulation. Whether you are a medical expert seeking a deeper understanding of endocrine function or an individual interested in learning about the science behind hormone guideline, this publication is a vital resource.
Hormonal Agents and Their Functions
Hormonal agents play important duties in the regulation and sychronisation of various physical procedures within the body. These chemical carriers are produced by endocrine glands and are launched into the bloodstream, where they take a trip to target cells or organs to exert their results. The features of hormones vary and include practically every aspect of human physiology.
One of the main functions of hormonal agents is to maintain homeostasis, which is the secure internal atmosphere needed for the body to function ideally. For instance, insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreatic, controls blood sugar degrees by advertising the uptake and storage space of sugar in cells. Another hormonal agent, cortisol, aids the body react to tension by enhancing blood sugar degrees and suppressing the body immune system.
Hormones likewise play vital functions in growth and growth. Growth hormone, produced by the pituitary gland, stimulates the growth of cells and bones, while thyroid hormonal agents manage metabolic process and affect the advancement of the nerve system - Best endocrinologist in austin. In addition, reproductive hormonal agents, such as estrogen and testosterone, are accountable for the growth and maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics and the regulation of the menstrual cycle
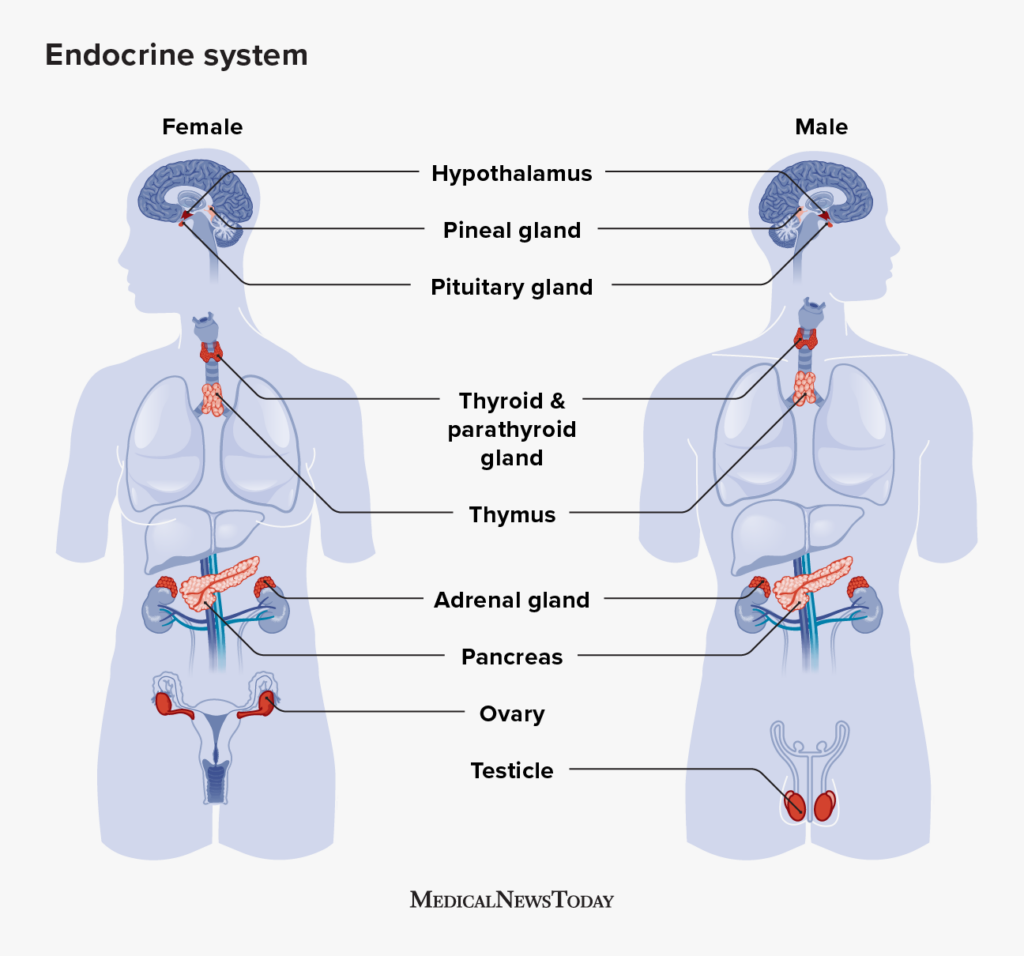
The Endocrine System: An Overview
Playing a critical role in the guideline and control of physical processes, the endocrine system is an intricate network of glands that generate and release hormonal agents right into the bloodstream. These glands, consisting of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes, secrete hormonal agents that work as chemical messengers, affecting numerous bodily features. The endocrine system works in conjunction with the nerves to maintain and control homeostasis, guaranteeing that the body's interior atmosphere remains steady.
The hypothalamus, situated in the brain, is considered the master regulator of the endocrine system. It generates hormones that boost or prevent the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, which consequently controls the task of other endocrine glands. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, generates hormones that regulate metabolism and energy equilibrium. The adrenal glands, situated atop the kidneys, generate hormonal agents that aid the body respond to stress and anxiety and regulate high blood pressure.

Policy of Hormone Manufacturing
The regulation of hormone production involves a complicated interplay in between numerous glands and responses mechanisms within the endocrine system. Hormonal agents are chemical messengers that play an important duty in maintaining homeostasis and coordinating various physical processes in the body. The production of hormones is firmly managed to make certain the correct functioning of the endocrine system.
The hypothalamus, situated in the mind, acts as a vital regulatory authority of hormone manufacturing. It releases hormones that inhibit the production or promote of hormones by the pituitary gland, which is frequently described as the "master gland" of the endocrine system. The pituitary gland, subsequently, produces hormonal agents that act on different target glands throughout the body, stimulating them to create and launch specific hormones.
Comments mechanisms additionally play a crucial duty in hormone regulation. There are 2 sorts of comments systems: negative comments and positive comments. Adverse comments helps keep hormone levels within a slim range. When hormone levels climb over or fall listed below the optimum range, the body sets off devices to either reduction or boost hormonal agent manufacturing, respectively, to restore equilibrium. Favorable comments, on the other hand, intensifies the production of hormonal agents in response to particular stimulations, such as giving birth.
Responses Loops in Hormone Regulation
Comments loops play an essential role in the law of hormone production. These loopholes include a series of communications between the endocrine glands, hormones, and target organs to keep homeostasis in the body. There are 2 sorts of comments loops: adverse comments and positive feedback.
Adverse feedback is the most typical kind of feedback loop in hormone regulation. It works by noticing the levels of a hormonal agent in the blood and adjusting hormonal agent manufacturing accordingly. When hormone levels rise over a specific threshold, the hypothalamus in the mind signifies the pituitary gland to lower hormonal agent production. This, consequently, reduces the excitement of the target organ, leading to a decline in hormonal agent secretion. Conversely, when hormonal agent levels drop listed below the limit, the hypothalamus boosts the pituitary gland to boost hormone manufacturing, recovering balance.
Favorable responses loopholes, on the various other hand, enhance hormonal agent manufacturing. This occurs when a hormone promotes the launch of more of the very same hormone, resulting in a quick increase in its degrees. Nonetheless, positive comments loopholes are much less common in hormonal agent law and are normally associated with details physiological procedures, such as giving birth and lactation.
Elements Affecting Hormonal Agent Equilibrium
Factors affecting hormone equilibrium consist of nutritional selections, way of living routines, and environmental exposures. These elements can have a considerable impact on the fragile equilibrium of hormones in the body, affecting various physical processes and general health.
Nutritional selections play a vital function in hormonal agent regulation. Eating a well balanced diet that consists of a selection of nutrients is crucial for keeping hormonal agent balance.
Appropriate rest is critical for hormone manufacturing and regulation, as interfered with sleep patterns can lead to discrepancies. In addition, persistent stress and anxiety can dysregulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, an essential gamer in hormonal agent regulation, leading to a waterfall of hormone discrepancies.
Conclusion
In verdict, comprehending the scientific research behind hormonal agent regulation is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Hormones play important duties in different physical functions, and their manufacturing is managed by complex responses loops.
The Science Behind Hormonal Agent Regulation: Insights From an Endocrinologist provides an extensive expedition of the elaborate procedures involved in hormonal agent regulation. It generates hormones that stimulate or inhibit the launch of hormonal agents from the pituitary gland, which in turn controls the task of other endocrine glands. It launches hormones that stimulate or prevent the manufacturing of hormones by the pituitary gland, which is usually referred to as the "master gland" of the endocrine system. The pituitary gland, in turn, creates hormones that act on various target glands throughout the body, stimulating them to produce and launch details hormonal agents.
When hormonal agent degrees climb over a particular limit, the hypothalamus in the brain signals the pituitary gland to decrease hormonal agent manufacturing. (Best endocrinologist near me)